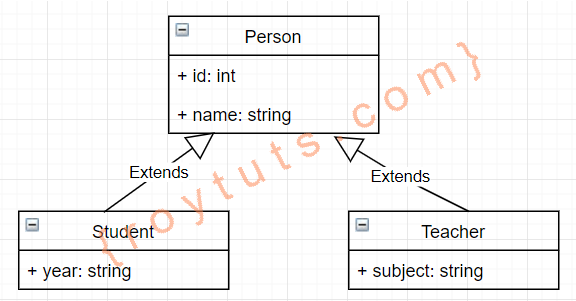
In Table Per Concrete Class Hierarchy will have the number of tables in the database equals to the number of derived classes. Once you save the derived class object, then derived class data and base class data will be saved in the derived class related table in the database.
You need tables only for the derived classes. For this in the hibernate XML mapping file you need to use one new element <union-subclass/> under <class/> tag. In this example, data will be saved only in student and teacher tables.
In the above hierarchy, three classes are involved where Person is the super class and Student and Teacher are subclasses with their own properties declared as instance variables.
Related Posts:
- Hibernate Inheritance – Table per Subclass Hierarchy
- Hibernate Inheritance – Table per Class Hierarchy
Prerequisites
Java at least 8, Maven 3.6.3, Hibernate 6.0.0.Alpha8, MySQL 8.0.22
Project Setup
Create a maven based project in your favorite IDE or tool. The name of the project is hibernate-inheritance-table-per-concreteclass.
The required dependencies in pom.xml file can be given as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.roytuts</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-inheritance-table-per-concreteclass</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>12</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>12</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>6.0.0.Alpha8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.22</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
MySQL Table
As the table per sub-class inheritance hierarchy requires a separate table for each sub-class so I am going to create two tables in MySQL database.
CREATE TABLE student (
id int unsigned COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci,
name varchar(50) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci,
year varchar(50) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
CREATE TABLE teacher (
id int unsigned COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci,
name varchar(50) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci,
subject varchar(50) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci;The id and name columns in the respective tables are values coming from person table.
Entity Classes
Here I am going to create the base entity class Person that will be extended by two sub-classes Student and Teacher and these sub-classes will inherit properties from the base class.
Person
The base class I am going to create as an abstract class. I am not using auto-increment value for id field so I am not using generation strategy for it.
I am specifying the inheritance strategy using annotation @Inheritance.
@Entity
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.TABLE_PER_CLASS)
public abstract class Person {
@Id
// @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private int id;
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
public Person() {
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}Student
The sub-class Student has the following signature. In this sub-class I have specified the table name as I am creating separate table for each subclass. I have specified the column names which should be derived from parent class using annotation @AttributeOverrides.
@Entity
@Table(name = "student")
@AttributeOverrides({ @AttributeOverride(name = "id", column = @Column(name = "id")),
@AttributeOverride(name = "name", column = @Column(name = "name")) })
public class Student extends Person {
@Column(name = "year")
private String year;
public String getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(String year) {
this.year = year;
}
}Teacher
The Teacher class has the following details with the derived column names specified.
@Entity
@Table(name = "teacher")
@AttributeOverrides({ @AttributeOverride(name = "id", column = @Column(name = "id")),
@AttributeOverride(name = "name", column = @Column(name = "name")) })
public class Teacher extends Person {
@Column(name = "subject")
private String subject;
public String getSubject() {
return subject;
}
public void setSubject(String subject) {
this.subject = subject;
}
}Hibernate SessionFactory
The singleton SessionFactory class is needed to get non-thread safe session object from it. Here I am using annotation based configuration for building the session factory and mapping the entity classes.
public final class HibernateUtil {
private HibernateUtil() {
}
private static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
if (sessionFactory == null) {
try {
Configuration configuration = configuration();
ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry = new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder()
.applySettings(configuration.getProperties()).build();
sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return sessionFactory;
}
private static Configuration configuration() {
Properties settings = new Properties();
settings.put(Environment.DRIVER, "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
settings.put(Environment.URL, "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/roytuts");
settings.put(Environment.USER, "root");
settings.put(Environment.PASS, "root");
settings.put(Environment.DIALECT, "org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect");
settings.put(Environment.SHOW_SQL, "true");
settings.put(Environment.FORMAT_SQL, "true");
settings.put(Environment.CURRENT_SESSION_CONTEXT_CLASS, "thread");
settings.put(Environment.HBM2DDL_AUTO, "update"); // or create
// Deprecated
// settings.put(Environment.QUERY_TRANSLATOR,
// "org.hibernate.hql.internal.classic.ClassicQueryTranslatorFactory");
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.setProperties(settings);
configuration.addAnnotatedClass(Person.class);
configuration.addAnnotatedClass(Student.class);
configuration.addAnnotatedClass(Teacher.class);
return configuration;
}
}Testing the Application
I am writing a class with main method to test the application for table per concrete class inheritance strategy.
public class HibernateInheritanceApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
Teacher t = new Teacher();
s.setId(1);
s.setName("Student");
s.setYear("1st Year");
t.setId(2);
t.setName("Teacher");
t.setSubject("Physics");
Session session = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().getCurrentSession();
Transaction tx = null;
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
session.save(s);
session.save(t);
tx.commit();
} catch (HibernateException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Running the above main class you will see the following output in console:
Hibernate:
insert
into
student
(name, year, id)
values
(?, ?, ?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
teacher
(name, subject, id)
values
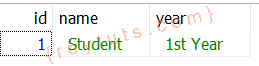
(?, ?, ?)Once the data have been successfully saved into the database the output will be:
Tables
student
teacher